As organizations strive to enhance their technological ecosystems, understanding the difference between multi-cloud and hybrid cloud paradigms becomes paramount. While both approaches promise flexibility and resilience, they cater to business operations and leverage their digital assets.
Multi-cloud and hybrid cloud are essential elements in the orchestration of modern IT ecosystems, offering unprecedented flexibility, cost-efficiency, and innovation. By strategically integrating these models, enhances the operational process and not only meets the current demands but also anticipates future growth and opportunities.
Cloud adoption among enterprise organizations is over 94%
Source: RightScale
This blog explores how multi-cloud vs hybrid cloud approaches, each play their distinct roles in modern enterprise architecture and the implementation of cloud strategies offers insights into optimizing scalability, control, and innovation in a world where cloud choices shape competitive advantage.
What is cloud computing?
Cloud computing is a technology that allows users to access IT resources such as servers, storage, databases, and software over the internet in a pay as you go method. Instead of owning and managing physical data centers and infrastructure, users can leverage remote servers maintained by cloud consulting service providers as required.
Organizations of every type, size, and industry utilize cloud for variety of use cases reaping benefits such as scalability, agility, cost efficiency, and rapid global deployment.
The stats given below explains the vision of business leaders in adapting the cloud computing usage in upcoming years.
What are the three main cloud delivery models?
-
-
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Builds basic blocks for IT, providing the highest level of flexibility and control of your IT resources. Users can rent virtual machines and pay for the time it is used.
-
Examples: Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines, Amazon EC2, Google Compute Engine.
-
-
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Removes underlying infrastructure management, allows focusing on deployment and management of your applications, and increases application lifecycle efficiency.
-
Examples: Microsoft Azure App Service, Google App Engine, AWS Elastic Beanstalk.
-
-
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Delivers complete product run. It is managed by service providers and offers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis.
-
Examples: Microsoft Office 365, Google Workspace, Salesforce.
Azure guide: IaaS, PaaS, SaaS
What is IaaS, Paas, SaaS in Azure Cloud? How can it help you and your business? Let’s get in and explore all the details about Azure.
What are the 4 types of cloud computing models for business growth?
Multi-cloud
Multi-cloud refers to the use of multiple cloud computing services from different providers within a single architecture. It involves combining public cloud services like AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform and private clouds, ensuring flexibility to optimize performance, avoiding vendor lock-in, and control costs.
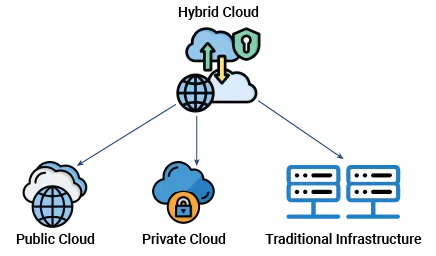
Hybrid cloud
Microsoft hybrid cloud architecture is a mix of on-premises infrastructure, private clouds, and public clouds allowing data to be shared quickly and securely across the cloud environment. It provides businesses with greater flexibility, scalability and cost optimization than traditional on-premises infrastructure setups.
According to the IBM Transformation Index: State of Cloud, more than 77% of business and IT professionals have adopted a hybrid cloud approach.
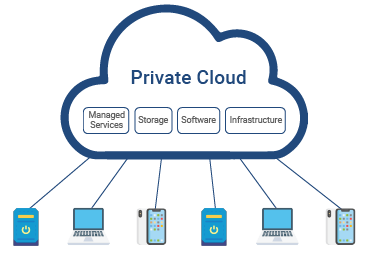
Private cloud
It is a cloud computing resources utilize by single business or organization located on company’s onsite data center. It is dedicated solely to one entity, providing a customized blend of computing resources and security protocols. Whether hosted on-premises or by a specialized provider, it offers enhanced control, data privacy, and flexibility, ensuring that your organization’s unique needs are met with precision and care.
Public cloud
It is owned and managed by third-party cloud service providers that deliver resources such as storage, computing power, and applications over the internet and shared among multiple organizations or users. Public clouds are typically known for their scalability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of access. Major public cloud providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
How does cloud computing work?
Cloud computing operates as a dynamic digital ecosystem where computational resources, such as storage and processing power, are delivered over the internet. It leverages:
- Remote servers: Resources are hosted on remote servers in data centers, not on local machines.
- Internet access: Services are accessed over the internet providing flexibility and scalability. Also, manages data virtually and from anywhere.
- On-demand services: Users can scale resources up or down based on their needs paying only for what they use.
Multi-cloud vs. hybrid cloud: What’s the difference?
| Aspect | Multi-Cloud | Hybrid cloud |
| Definition | Utilizes multiple cloud service providers to meet various needs. | Combines public cloud services with on-premises infrastructure. |
| Cloud providers | Involves two or more different cloud providers (e.g., AWS, Azure, Google Cloud). | Combines public cloud services with on-premises infrastructure. |
| Primary focus | Avoids vendor lock-in, leverages best-of-breed services from various providers | Balances workloads between public and private clouds to optimize performance and security. |
| Management complexity | Higher due to managing multiple cloud platforms with different interfaces and tools. | Lower, as it involves fewer environments with potential for unified management through hybrid cloud solutions. |
| Data and workload placement | Data and workloads are distributed across various cloud providers based on service capabilities and pricing. | Data and workloads are placed according to compliance, security, and performance needs, with some residing on-premises and others in the cloud. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility in choosing specialized services and adjusting resources. | Flexibility in running workloads across different environments while maintaining control over sensitive data. |
| Cost considerations | Cost-effective by optimizing service usage but may incur higher management costs. | May involve higher costs if managing and integrating multiple environments but can reduce costs by optimizing resource allocation. |
| Security and compliance | Requires consistent security policies across different cloud providers, which can be complex. | Enables a more controlled environment for sensitive data while leveraging public cloud benefits for other workloads. |
| Disaster recovery | Each provider has its own disaster recovery solutions, which may require integration | Allows for integrated disaster recovery strategies across on-premises and cloud environments. |
| Use cases | Ideal for leveraging diverse cloud services, avoiding vendor lock-in, and optimizing specific workloads. | Best for organizations needing to maintain a balance of on-premises and cloud resources for flexibility, control, and compliance. |
Now, that the concepts are clear, let’s understand the benefits of using Microsoft Azure Cloud, one of the most popular among businesses.
Azure in a multi-cloud strategy
Azure’s multi-cloud strategy involves working seamlessly with other cloud platforms like AWS (Amazon Web Services) and Google Cloud. This integration allows businesses to leverage the strengths of multiple cloud providers while maintaining a cohesive operational framework. Here’s how Azure facilitates this:
-
Interoperability:
It offers services and solutions that enable interoperability between its platform and other cloud services. This means that data and applications can be shared and operated across different clouds, enhancing flexibility and avoiding vendor lock-in.
-
Cross-cloud applications:
Azure supports building and deploying applications that span multiple cloud environments. For example, an application might use Azure for its data storage and processing needs while leveraging AWS for specific computational tasks.
Implementing Azure in a hybrid cloud strategy for successful business
Azure offers a range of hybrid cloud solutions designed to seamlessly integrate on-premises infrastructure with Azure’s cloud services. These solutions enable organizations to build, deploy, and manage applications and workloads across both on-premises and cloud environments. Here’s how Azure offers benefits:
- Seamless integration and scalability
- Cost efficiency
- Security and compliance
- Business continuity
Multi-cloud use cases with Azure
-
-
Vendor lock-in avoidance with Azure
-
Using Azure in a multi-cloud strategy allows organizations to diversify their cloud portfolio, reducing reliance on a single provider and giving them the flexibility to leverage the best features of each platform.
-
-
Optimized workloads across Azure and other clouds
-
Businesses optimize their cloud strategy by deploying specific workloads on Azure that benefits from its strong enterprise tools, while using other cloud providers for different needs, such as AWS for serverless computing or Google Cloud for AI.
-
-
Enhanced disaster recovery with Azure
-
Azure provides disaster recovery solutions that seamlessly integrate with multi-cloud architecture. It ensures data and applications are replicated across multiple clouds, minimizing downtime, and enhancing resilience in case of failures.
-
-
Global reach and low latency with Azure
-
Azure’s extensive global infrastructure allows organizations to distribute applications across various regions, in combination with other cloud providers, to ensure low latency and improved user experience worldwide.
-
-
Compliance and data sovereignty with Azure
-
Azure’s compliance offering and global data center footprint make it ideal for organizations needing to meet specific regulatory requirements by storing data in designated regions, in combination with other cloud providers.
-
-
Agility and innovation using Azure
-
By integrating Azure into a multi-cloud strategy, businesses can take advantage of Azure’s cutting-edge services, such as Azure Machine Learning or Azure AI, while also experimenting with innovations from other cloud providers.
Importance of a multi-cloud strategy
Discover how a multi-cloud strategy can enhance disaster recovery and backup capabilities, safeguard business operations, and optimize performance. Learn practical insights on implementing an effective multi-cloud plan and how SaaS providers can help.
Hybrid-cloud use cases with Azure
-
-
Data sovereignty and compliance with Azure
-
Azure enables organizations to keep sensitive data within their on-premises or private cloud environments while using Azure’s public cloud for scalable compute resources, ensuring compliance with regional data protection regulations.
-
-
Disaster recovery and business continuity using Azure
-
Azure Site Recovery allows businesses to replicate on-premises workloads to Azure, providing a seamless disaster recovery solution that ensures critical applications and data are quickly restored in the event of an outage.
-
-
DevOps and application deployment with Azure
-
Azure DevOps supports hybrid cloud environments, allowing teams to manage CI/CD pipelines that deploy applications across both on-premises infrastructure and Azure, enhancing agility and reducing deployment times.
-
-
Bursting workloads to Azure
-
Organizations can utilize Azure’s scalable cloud resources to handle peak workloads, extending their on-premises capacity to the cloud when needed, ensuring consistent performance without overprovisioning.
-
-
Big data and analytics with Azure
-
Azure Synapse Analytics enables businesses to analyze massive datasets stored on-premises while leveraging the cloud’s power to perform complex analytics and machine learning tasks, all within a hybrid cloud architecture.
-
-
Hybrid SaaS solutions on Azure
-
Azure enables hybrid SaaS models where core functions are hosted in the cloud, while maintaining integration with on-premises systems, allowing businesses to operate seamlessly across environments
Leverage the benefits of cloud!
The rapid growth of Azure cloud is promising innovation and at the same time raises new challenges. At Softweb Solutions, we are committed to developing innovation with operational efficiency.
As businesses navigate their digital transformation journeys, understanding these distinctions will be key to architecting a cloud strategy that not only meets their immediate needs but also adapts to the evolving demands of a dynamic market. To know more, talk to our experts!