Mixed reality (MR) application is a hybrid of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) that has come a long way since its inception. Realizing the combinational potential of these technologies, in recent years, medical practitioners have begun exploring MR capabilities in the healthcare sector. This post will discuss practical mixed reality applications in medical training, education and preprocedural planning during surgery.
In 2025, the global mixed reality market will increase to about 3.7 billion U.S. dollars and the healthcare sector will hold the majority. – Statista
Applications of MR in healthcare
In operating rooms, clinics, hospital wards and medical training settings, mixed reality speeds up diagnosis, increases access to healthcare facilities, cuts down on infection transmission as well as enhances medical care outcomes. It can use holographic overlaying of images and data onto real-life situations such as surgical operations, remote consultation and treatment, opening new avenues in healthcare. Let us check out the trending use cases of mixed reality in healthcare segments.
“What makes mixed reality particularly suitable for use in healthcare are its 3D capabilities, with scalable objects that can be interacted on simultaneously by several participants and its ability to provide a deeper and better understanding of complex issues.” – Prof. Andrew Perkis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology
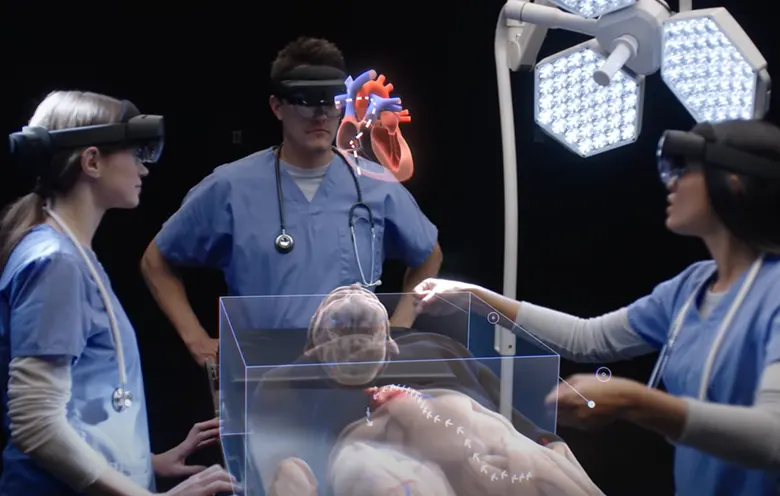
MR in the cardiology field
It makes intuitive sense that educational fields would benefit from mixed reality technology. There have been a few MR-derived training applications launched in the past. The first MR healthcare application created interactive visualizations enabling pediatric cardiologists to demonstrate complex congenital heart problems to their trainees/patients virtually.
Additionally, pre-procedural surgical planning processes are rapidly incorporating mixed reality technologies. The presentation of cardiac digital imaging and communications in medicine (DICOM) images in a three-dimensional virtual environment. It gives the user a better understanding of depth perception, requiring precise volume measurements and better data management.
Before cardiac procedures, computed tomography or magnetic resonance tests are primarily connected. But with MR techniques it takes less time to understand data with comparable accuracy, when compared to flat screen monitor displays, three-dimensional displays are produced.
In cardiac surgical technique, MR plays a key role. Consider a situation in which a doctor using a Microsoft HoloLens headset can interact with the hologram using hand movements and benefit from a wider field of view. Three-dimensional echocardiography data is delivered in holographic form in real-time to support heart surgery. Additionally, two-dimensional echocardiography and traditional computer monitors in the operation room show the patient’s angiography.
Autism therapy
MR is used in an “autism glass” project of the medical school of Stanford University to help autistic kids understand their emotions and automate facial expression identification. Soon, it is expected to increase its precision, eventually making it possible for users to utilize it without using any immersive headset.
Pain relief for the phantom limb
Researchers from Aalborg University in Denmark undertook a study to understand pain relief for the phantom limb. It is to determine whether deluding an amputee’s brain into thinking it still controls their missing limb can assist in reducing the agony associated with phantom limbs. When a patient moves his arm, the virtual arm moves in lockstep with them, allowing the patient to control the amputated limb with his brain.
Transforming surgery process
The convenience of seeing the patients’ 3D computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans directly is made possible by mixed reality technology for surgeons. It will make it easier for surgeons to identify the precise area of the patients’ anatomy where the procedure is practiced quicker to carry out the surgery successfully in emergencies.
Immersive learning for nurses
It is essential for the healthcare sector to employ skilled nurses for better patient care delivery. The most efficient way to teach and prepare nurses to react appropriately in situations they encounter is through simulations. A nursing student may experience those unique or uncommon circumstances in a mixed reality that might be challenging to plan for in actual clinical settings.
Such lifelike simulations are significantly less expensive than conventional nursing simulation equipment. For instance, there are applications in the market that teach medical practitioners how to diagnose and treat medical problems by using patient’s holograms.
Medical training using 3D holograms
Mixed reality for medical training has gained significant traction in recent years in academic settings where it helps lecturers teach several courses and skills. Before performing procedures on patients, students can also sharpen their abilities. Mixed reality in surgery allows doctors to complete the treatment faster and with a higher degree of success.
With the help of 3D holograms, NUS Medicine (Singapore) developed Project Polaris. It aims to incorporate MR into their learning experience, create a realistic clinical scenario and provide their students with a visual representation of clinical procedural skills like inserting a cannula and catheters in the male and female urinary tracts.
Improved surgery on the anatomy
Pre-operative simulations are made easier by MR, which creates customized 3D models for each patient and visualizes the inside anatomy in a fully immersive environment. In complex surgical operations like reconstructive surgeries, holographic overlays can substantially help surgeons to examine the bones and determine the flow of blood arteries.
Quick diagnostics
MR enables medical practitioners to view the vocal patient history to discuss with medical specialists and record it using MR headsets. Furthermore, by eliminating the need for doctors to review physical reports, MR-powered headsets can even analyze data and deliver findings to them in real-time, resulting in faster and more precise diagnoses.
Why do you think it would be risky to use MR?
Healthcare applications range from home care to acute care facilities. Healthcare professionals face a few difficulties as they get ready to integrate MR technology, even though these innovations predict to save costs and improve patient outcomes and satisfaction.
Market growth is likely to be constrained by several factors such as:
- Shortage of qualified medical professionals
- High investment costs
- Technical difficulties
- Establishing interoperability with existing systems
- Defining reimbursement schemes
- Creating a secure environment
- Concern over data loss
Therefore, it is advisable to begin looking into constructing healthy apps that are critical to addressing your healthcare services.
Looking ahead
Despite these obstacles, mixed reality adoption globally is exponential because of elements such as the fast development of sensor technology, consumer acceptance growth, MR apps viability in medical treatment and healthcare professional’s productivity.
Mixed reality apps can take the healthcare sector to another level with advantages such as increased operational effectiveness, higher-quality services and lessened human effort. Check out our mixed reality in healthcare services to know more.