Data is the lifeblood of modern businesses. It drives decision making, improves the customer experience and helps organizations stay competitive. The constant flow of large amounts of data is difficult to manage and analyze effectively. This is where the pivotal role of data pipelines comes into play.
What is a data pipeline?
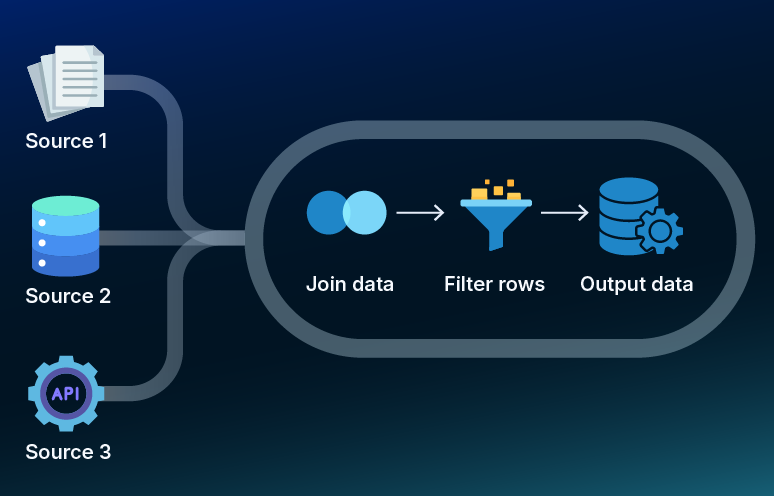
Simply put, a data pipeline strategy is a set of steps that move data from one place to another. It extracts information from its repository, transforms the data into a beneficial format and positions it where it’s required. It can involve ETL or ELT processes and other operations to facilitate the flow of data. You can think of it as a well-organized delivery system for information.
You can build data pipelines using various tools and technologies. Some popular options include Apache Kafka, Apache Airflow and Apache NiFi. These tools provide a framework for data pipeline designing, scheduling and monitoring. They also offer features like data validation, error handling, and data lineage, that are essential for maintaining data integrity and traceability.
Suggested: Don’t miss out! ETL vs. ELT – the crucial differences you need to know now!
Why do you need a data pipeline?
Your enterprise might seek operational efficiency and strategic insights, which makes data pipelines indispensable. These pipelines, especially the big data pipelines, compile and make data easily accessible for better usability.
ETL, ELT and real-time data pipelines are important for improving your data quality and transforming unstructured data into accurate insights. The design and implementation of best data pipelines requires careful consideration of data sources, transformation logic and storage systems.
What are the types of data pipelines?
There are several data pipelines. Let’s discuss the two main types of data pipelines: batch and streaming. Batch data pipelines are used to process large volumes of data at regular intervals. Streaming data pipelines are used to process data as it is generated.
Batch data pipelines
Batch data pipelines handle large datasets at regular intervals, like loading into a data warehouse or creating reports. They are set to run at certain times, such as daily or weekly.
Streaming data pipelines
Streaming data pipelines are ideal for real-time data processing. They are perfect for tasks such as real-time monitoring and fraud detection. This pipeline scrutinizes data right after it is created, providing immediate understanding.
With data engineering, you can create, optimize and maintain these pipelines. It helps ensuring a seamless flow of data for informed decision making.
Learn more about: data engineering: What it is and why it matters
Key use cases of data pipeline
A well-designed data pipeline ensures seamless data flow, enhancing efficiency and decision-making across various domains. Here are some essential data pipeline use cases:
- Transaction processing and storage: You can facilitate the processing and movement of transaction data for insightful reporting and real-time analytics.
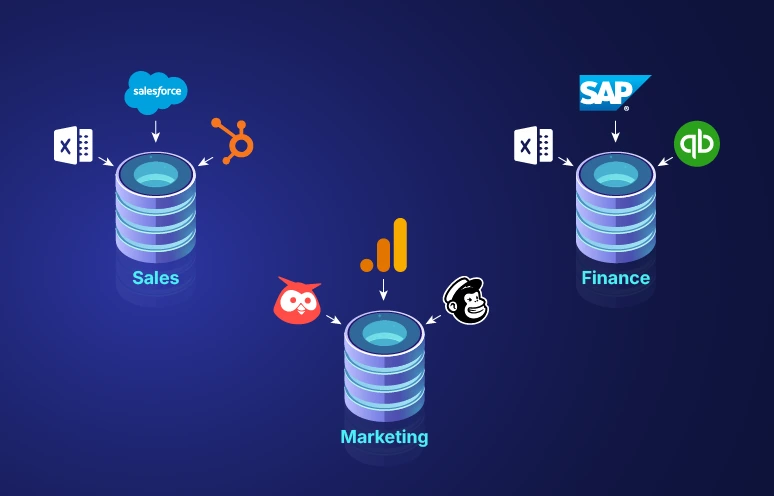
- Creating a unified view: Consolidates your data from myriad sources into a singular data store, providing organizations with a unified source of truth.
- Data visualization: Aggregates the requisite data in real-time for you to create compelling visualizations, a crucial tool for delivering comprehensive insights.
- Machine learning: Serves as a pipeline for you to ingest source data into machine learning algorithms, thereby enhancing accuracy.
- Improving backend systems: Offload data to expansive data stores to help you bolster the performance of backend systems.
- Exploratory data analysis (EDA): Consolidate the requisite data for detailed analysis and investigation of data sets.
- Ensuring data quality: Elevate your data quality, reliability, and consistency through cleaning and validation tasks during data movement.
What are the components of a data pipeline?
A structured data pipeline design enables seamless data flow from ingestion to consumption while ensuring accuracy, security, and scalability. Here are the key components of a robust data pipeline:
- Data sources: The origination points of data, ranging from databases and SaaS applications to IoT devices and social media.
- Data ingestion: The process of transferring data from sources into the data pipeline, occurring either in batches or in real time.
- Data processing: The transformative process of preparing data for analysis or storage, involving cleaning, filtering and aggregating tasks.
- Data storage: The repository where processed data resides, spanning data warehouses, data lakes, and data marts.
- Data consumption: The process to ingest data and make it available for analysis through dashboards, reports, machine learning models, and other applications.
- Data governance: Overarching frameworks such as audit trails, access control, and encryption ensure data accuracy, security, and regulatory compliance.
How to design a data pipeline in eight steps
When you plan step-by-step to develop data pipelines, the decisions you make at the beginning can affect the outcome later. This part is a guide to help you ask the correct questions at the beginning of the data pipeline design process.
Step 1: What’s your goal?
When you are starting to design your data pipeline, the first thing you need to figure out is what you want it to achieve. It’s like setting the stage. Questions that can help at this point include:
- What exactly are you trying to achieve with this data pipeline?
- How will you know if it’s doing well?
- What are you going to use this data for—reports, data analytics, machine learning?
Step 2: Where’s your data coming from?
Now that you know what you want, you have got to think about where your data is coming from. Some questions to consider:
- Where’s all this data going to come from?
- What kind of format will it be in (like flat files, JSON, XML)?
- How are you going to connect these data sources?
Step 3: How are you getting the data in?
Once you’ve figured out where your data is coming from, you have to decide how you’re going to grab it. Some things to think about:
- Which protocol to use to communicate with these data sources (like HTTP, MQTT, gRPC)?
- Do you need any other tools to grab the data?
- Are you storing data in a temporary place before it goes to its final home?
- Is the data coming in chunks or in real-time?
Step 4: What are you doing with the data?
Once you have obtained your data, you need to make it valuable. Questions to consider:
- How are you processing the data (cleaning, formatting, transforming)?
- Are you adding more details to the data?
- Are you using all the data or just some of it?
- How do you get rid of stuff you don’t need?
Step 5: Where does it all go?
Once you have processed your data, you must determine its designated location. Think about:
- Are you using big data storage like data warehouses or data lakes?
- Is it going to be in the cloud or on your own servers?
- Which storage option is best for what you’re trying to do?
- What format are you keeping the final data in?
Step 6: How does everything flow?
Now that you have a plan, you need to determine how everything fits together. Some things to think about:
- What must happen before something else can start?
- Can some things happen simultaneously?
- How do you deal with things if they go wrong?
Step 7: Keeping an eye on things
Once your data is flowing, it is important to ensure its smooth operation. Questions to consider:
- What do you need to keep an eye on?
- How do you make sure your data is safe?
- What if someone tries to mess with your data?
- Is everything happening according to schedule?
- Who’s in charge of keeping an eye on things?
Step 8: How are you using the data?
The last step is figuring out who’s using the data and how. Some things to consider:
- What’s the best way to use the data you’ve got?
- Do you have everything you need for what you want to do?
By following these steps, you lay the foundation for optimizing data pipelines, ensuring efficiency, accuracy, and seamless execution from start to finish.
Softweb Solutions: Elevating your real-time data pipeline experience
In the realm of data management, Softweb Solutions can be your trusted partner in streamlining processes and eliminating the need for complex IT interventions or convoluted software installations. Our user-friendly approach caters to both novices and those seeking a seamless process, empowering businesses to harness the full potential of their data.
Our team of data engineers stands ready to assist you in importing and analyzing data from diverse sources, providing a holistic understanding of customer perceptions. If you know about the data pipeline best practices and want to build a robust one aligned with your business model, our experts are at your disposal. Connect with us to explore how Softweb Solutions can be your guiding force in data pipeline optimization for sustained success.