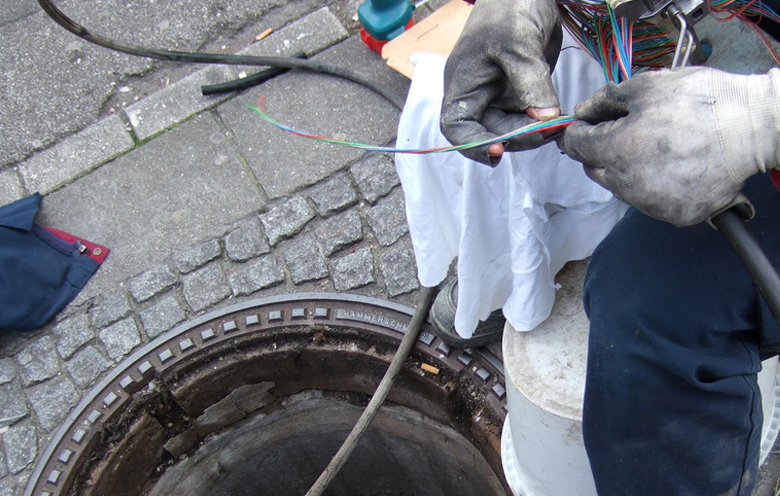
August 17, 1858, the first official message was sent from Queen Victoria to President James Buchanan. It took 17 hours and 40 minutes for the 509-letter message to transmit from London to Washington. However, that was significantly faster than the typical 12 days period a ship used to take to traverse the ocean. In the 1880s and 1890s, electricity was considered as an expensive novelty. Today, data and electricity travel as fast as the blink of an eye.
Thanks to 750,000 miles of cable and still growing network, which supports our communication and entertainment needs. Electricity and data continue to position themselves as the ‘fuel’ of the future, so does the need for reliability on cables. With no look back in urbanization, industrialization, electrification of rural areas and data-intensive activities, the future of the cable market looks attractive.
The global market of power distribution cables will reach US$ 130 billion by 2024, from US$ 90.7 billion in 2019.
– Global Power Distribution Cables Market Report
With tons of opportunities in the industrial, residential, utilities and commercial sectors, top cable manufacturers and distributors have become aggressive in site identification and expanding their cable network. While they have become busy in engineering the cable network, many companies overlook the crucial aspect of asset lifecycle – operations and maintenance (O&M). With the expertise cultivated in trending technologies, such as IoT, big data and AI – our business analysts and solution architects have closely looked at the challenges that cable asset managers and maintenance engineers may face during O&M. Below is the list of issues and how the implementation of IoT technology or an IoT platform can solve them.
1. Quick response and turnaround time
2. Less maintenance
3. High efficiency
1. Quick response and turnaround time
Different cables have different average ages. For example, the average age of butyl rubber cable is 42 years. HMWPE has a lifespan of 33 years. XLPE has a life expectancy of 23 years and XLPE Jkt has an estimated age of 18 years. Cables and cable accessories are constantly subjected to thermal, electrical, environmental and mechanical stresses. These stresses often lead to insulation degradation and with poor maintenance, it results in defects and often cause cable breakdowns.
Nevertheless, employing planned maintenance and replacing cables and associated assets purely based on age is unnecessary and consume a high cost. Naturally, stress conditions vary in different areas, so does the age of cables and accessories. It suggests that there can be a good proportion of cable assets that are working in their suitable environments, thus providing extended service life. On the other hand, with the downtime in cables, network owners have to face lost revenue, diminished customer service and reduced competitive advantage. An hour of downtime costs around $42,000 per hour, on average, according to Gartner. And if an enterprise is challenged to expand its annual uptime, even just 0.09%, maybe from 99.9% to 99.99%, it needs to reduce downtime by eight hours. That’s equal to saving $336,000 annually of an enterprise. How can a cable asset manager or safety engineer empower a company to reach there?
Using relevant sensors, protocols and other required IoT technologies, one can get alerts about failure forecasts. Using IoTConnect, a user can set rules and commands and assign an expert to be notified in case of a downtime event. With this, a company will not only be able to address the issue before time but also increase its competitive advantage.
2. Less maintenance
Installers know the impact of voltage fluctuations, short circuit events and various stress conditions on cable assets; however, how many of them can monitor these parameters that ensure less maintenance?
Cable fault location is generally identified either via off-line and on-line time domain reflectometry methods or based on time of arrival of partial discharge signals associated with a fault. For offshore wind farms, the technique of distributed acoustic sensing was in practice. Today, under a smart cable fault detection solution, two inductive sensors are used to sense the electromagnetic waves originating from a fault position, which is more accurate, timesaving and cost-effective. Such IoT-based methods assure more effective maintenance.
Using a smart cable fault detection solution, a facility manager gets access to centralized system monitoring, heat and flame alerts on mobile and pin-pointed location of the fault.
3. High efficiency
To drive exceptional results and inspire excellence, count everything. For example, many PILC cables installed in the 1920s do not yet show signs of cable insulation failure. On the other hand, many modern XLPE cables are expected to be in service for 40+ years under normal circumstances. However, in the presence of water/moisture, those cables showed a life of only 15-25 years. It is also presented that most cable asset failures like joint, fuse, power switch, load switch, transformer, voltage transformer and low voltage occur in summer and autumn.
Can any action be taken with such historical data? Yes, cable assets operators can make failure forecasts based on Weibull analysis and Crow-AMSAA plots.
Contact our team of experts if you have more concerns or would like to discuss your specific requirements.